Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a transformative shift away from traditional banking by leveraging blockchain technology to create an open and accessible financial ecosystem. Here’s a detailed exploration of how DeFi is reshaping traditional finance:
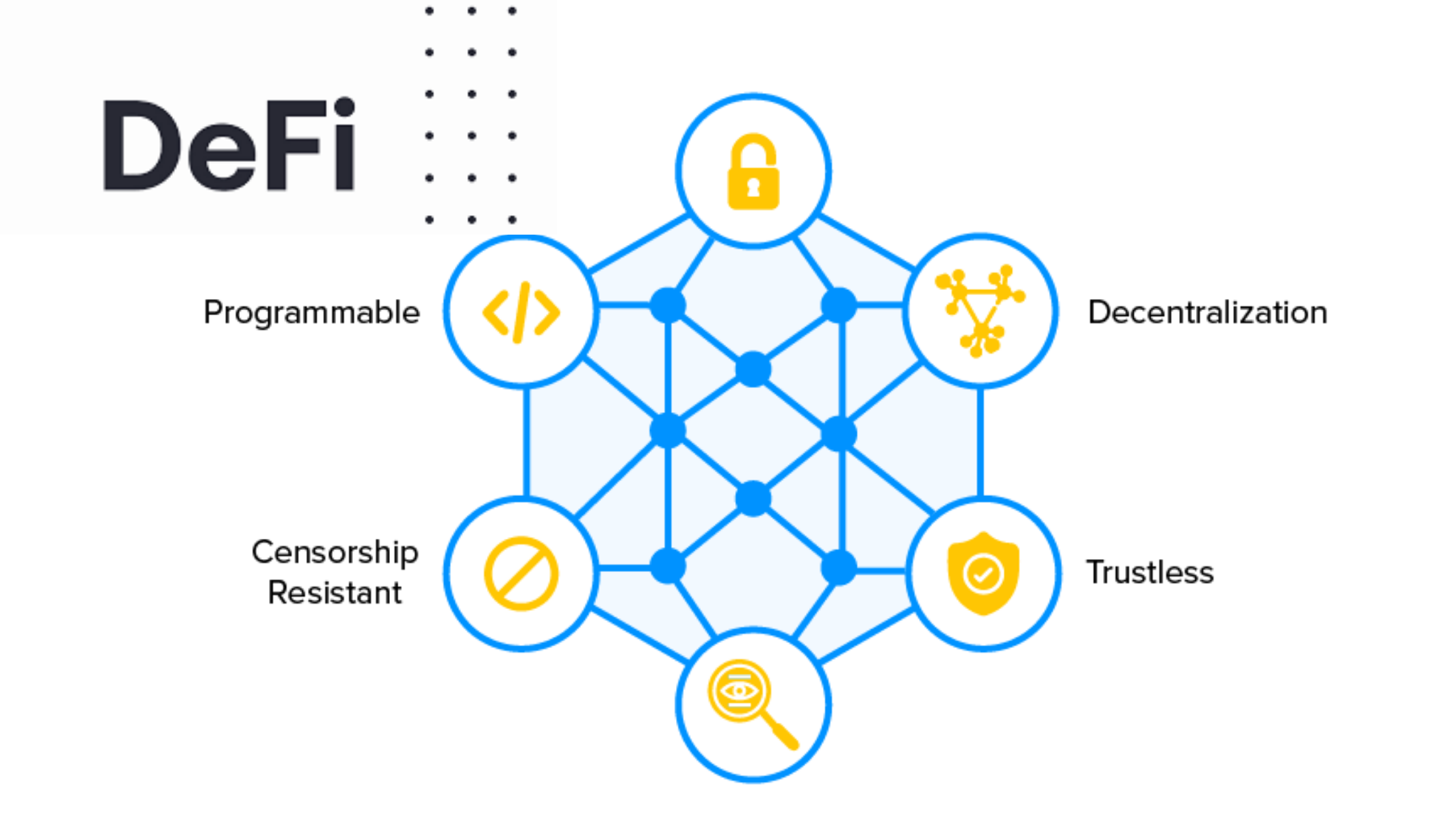
Decentralization:
- Removal of Intermediaries: DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks or financial institutions. Transactions are conducted peer-to-peer through smart contracts on blockchain platforms, ensuring greater transparency and reducing counterparty risk.
- Global Accessibility: DeFi platforms are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, enabling financial inclusion for underserved populations without requiring a traditional bank account.
Key Components of DeFi:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs facilitate cryptocurrency trading directly between users, allowing for seamless and secure asset exchange without relying on centralized exchanges.
- Lending and Borrowing: DeFi protocols enable individuals to lend their crypto assets in exchange for interest or borrow assets using their crypto holdings as collateral. Smart contracts automate these processes, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Stablecoins: These are cryptocurrencies designed to minimize price volatility, often pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar. Stablecoins play a vital role in DeFi by providing a reliable medium of exchange and store of value within the ecosystem.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs): AMMs use algorithms to enable liquidity provision and trading on DEXs. They allow users to trade assets directly against liquidity pools instead of order books, promoting efficiency and reducing slippage.
Benefits of DeFi:
- Accessibility: DeFi opens up financial services to a global audience, including those who are underserved or excluded by traditional banking systems.
- Transparency: Transactions on blockchain networks are transparent and immutable, enhancing trust and reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Innovation: DeFi fosters rapid innovation through open-source development and composability of protocols, enabling the creation of new financial products and services.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Security Risks: DeFi platforms are susceptible to smart contract vulnerabilities and hacks, highlighting the importance of robust security measures and auditing practices.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: DeFi operates across borders, posing challenges for regulatory compliance and oversight. Regulatory frameworks need to evolve to address the unique characteristics of decentralized finance.
- Scalability: As DeFi gains popularity, scalability issues on blockchain networks like Ethereum may arise due to network congestion and high transaction fees.
Future Outlook:
- The DeFi ecosystem is still in its nascent stages but is experiencing rapid growth and innovation. Continued development of layer 2 scaling solutions and interoperability protocols will enhance the scalability and usability of DeFi applications.
- Collaboration between DeFi projects, traditional financial institutions, and regulatory bodies will be crucial in shaping the future of decentralized finance and integrating it into the broader financial landscape.
In summary, DeFi is revolutionizing traditional banking by offering a decentralized alternative that promotes financial inclusion, transparency, and innovation. While challenges exist, the potential for DeFi to democratize access to financial services and reshape global finance is substantial, driving ongoing exploration and adoption across the industry.











+ There are no comments
Add yours